

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Jointly Owned Property in Dubai?
- Legal Framework Governing Joint Ownership
- Benefits of Shared Property Ownership
- Eligibility Requirements for Joint Ownership
- Step-by-Step Process for Jointly Owned Property Registration in Dubai
- Documentation Checklist
- DLD Smart Services for Joint Ownership
- Key Platforms: Title Deeds, Oqood, and Mollak
- Case Study: A Successful Shared Property Purchase
- Mistakes to Avoid in Joint Property Ownership
- Fees and Charges Involved
- Risks and Legal Safeguards
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- Partner with Homecubes for Smart Co-Ownership Solutions
Introduction
The idea of co-owning a property in Dubai has gained traction among investors and families alike. Whether you’re buying with your spouse, business partner, or sibling, understanding the ins and outs of Jointly Owned Property Registration Dubai is essential for a smooth transaction.
This guide explores the legal, procedural, and financial dimensions of shared property ownership registration in Dubai, covering everything from legal frameworks to smart service platforms. In 2025, joint ownership has become more than just a legal formality—it is a strategic investment model enabling diverse buyers to co-hold real estate assets with security, clarity, and legal protection.
Looking to set up your business in Dubai?
With DMCC, enjoy proximity to surrounding markets, a centralised time zone, and a business-friendly tax environment. Talk to our experts at our #MadeForTrade Live event on 11 June and gain exclusive insights into our easy business setup… pic.twitter.com/CFeCrX7pCe
— DMCC (@DMCCAuthority) June 2, 2025
Dubai’s dynamic real estate market has grown to accommodate innovative co-ownership models. As such, understanding the nuances—from eligibility to DLD’s evolving registration portals—is critical to successful, risk-free investment.
What is Jointly Owned Property in Dubai?
Joint ownership in Dubai refers to legal property co-ownership between two or more parties. It can apply to both completed and off-plan properties. In simple terms, it’s one property with two owners in Dubai, each holding a defined share of the asset.
There are two main types of joint ownership:
- Tenancy in Common: Owners hold individual shares which can differ in proportion. Each owner can sell or bequeath their share.
- Joint Tenancy: Each party has equal ownership, and rights transfer automatically to the surviving co-owner upon death.
Joint ownership applies to residential, commercial, and mixed-use properties and is governed by clear legal provisions under Dubai law.
Legal Framework Governing Joint Ownership
Dubai’s property sector is regulated under:
- Law No. (27) of 2007 on Jointly Owned Properties
- Law No. (6) of 2019 which updates provisions and clarifies rights of owners
- Oversight by the Dubai Land Department (DLD) and Real Estate Regulatory Agency (RERA).
- A full understanding of the RERA’s role in Dubai real estate as well as DLD’s is essential for all market participants.
These laws ensure:
- Maintenance of shared facilities in multi-unit developments
- Owner voting rights in jointly owned property decisions
- Rules for property management and service charges
For example, Law No. 6 clearly assigns responsibility for service fees, management roles, and owner obligations in shared buildings and communities.
Benefits of Shared Property Ownership
- Affordability: Lower capital outlay per individual allows access to premium assets.
- Shared Responsibilities: Costs like maintenance and utilities are divided among co-owners.
- Flexible Investment: Co-owning allows multiple investors to participate without owning a full unit.
- Legal Protection: DLD-issued title deeds clearly state each party’s share.
- Exit Options: You can legally sell your share, provided you follow consent rules and notify other owners.
- Estate Planning: Co-ownership enables wealth distribution among family members.
This structure is especially beneficial for expatriates, young professionals, and family trusts.
Eligibility Requirements for Joint Ownership

To register a jointly owned property in Dubai, you must:
- Be a UAE resident or a foreigner purchasing in a designated freehold area
- Submit valid Emirates ID or passport copies
- Not exceed four owners per property (as per latest DLD guidelines)
- Provide a notarized co-ownership agreement (recommended)
- Be clear about your share percentage and rights of use
Financial eligibility also includes either proof of funds or a joint mortgage application if financing is involved.
Step-by-Step Process for Jointly Owned Property Registration in Dubai

- Choose a Property: Select from freehold areas like Downtown Dubai, Dubai Marina, or Business Bay.
- Sales Agreement: All co-buyers must sign the SPA (Sales and Purchase Agreement)
- Payment & Finance: Either pay upfront or secure joint mortgage financing
- DLD Application: File for jointly owned registration via DLD’s online portal or a trustee center
- Document Verification: DLD validates your documents and checks co-ownership structure
- Fee Payment: Pay 4% of the property value + admin fees
- Title Issuance: DLD issues a deed showing all owners and their shares
The entire process typically takes 3–10 working days if all documents are in order.
Documentation Checklist
- Emirates IDs or passports of all co-buyers
- Sales and Purchase Agreement (SPA)
- Proof of payment or bank pre-approval for mortgage
- Co-ownership agreement (optional but recommended)
- NOC from developer (for off-plan properties)
- Completed DLD application form
- Power of Attorney (if acting on behalf of others)
Missing or mismatched information can delay title issuance.
DLD’s Key Platforms: Title Deeds, Oqood, and Mollak
- Title Deeds – Final proof of ownership issued by DLD. Includes each owner’s name and share.
- Dubai REST App – view ownership records, apply for services
- Oqood: Used for registering off-plan units. Ensures legal recognition before project completion.
- Mollak: Centralizes shared property services. Tracks payments, managed service providers, and records ownership updates.
Owners should become aware of the rules through a comprehensive guide to Mollak system in Dubai. As a rule of thumb, owners must register for Mollak access once the property handover process completes.
Case Study: A Successful Shared Property Purchase
Profile: Two entrepreneurs from Canada and the UAE co-purchased a penthouse in Business Bay for AED 4.5 million.
- Ownership Split: 60% and 40%
- Agreement: A lawyer drafted a co-ownership agreement with exit terms
- Tools Used: Dubai REST and Mollak for transparency
- Outcome: Registered within 8 days; property rented for AED 250K/year; profits distributed annually
This example highlights the importance of legal clarity, proper planning, and smart tech use.
Mistakes to Avoid in Joint Property Ownership
Avoiding costly mistakes is crucial when entering a co-ownership agreement. Here are the most common pitfalls:
- Skipping Legal Agreements: Always sign a co-ownership agreement detailing each owner’s responsibilities, use rights, and exit clauses.
- Verbal Agreements Only: Without documentation, disagreements have no legal backing.
- Unequal Investment With No Clarity: Financial imbalance without written acknowledgment can create future disputes.
- Ignoring Service Charges: These are mandatory and must be paid regularly via Mollak.
- Unregistered Changes: Selling or transferring shares without DLD notification renders the transaction invalid.
- Not Notifying Other Owners Before Selling Your Share: This violates co-ownership etiquette and often leads to legal challenges.
- Disregarding Mortgages on Joint Properties: All parties are usually liable unless specified otherwise.
- Incorrect Title Deed Details: Ensure each name and ownership percentage is correctly recorded.
- Delays in Registration and Documentation Submission: Time-sensitive filings are crucial for legal standing.
Fees and Charges Involved
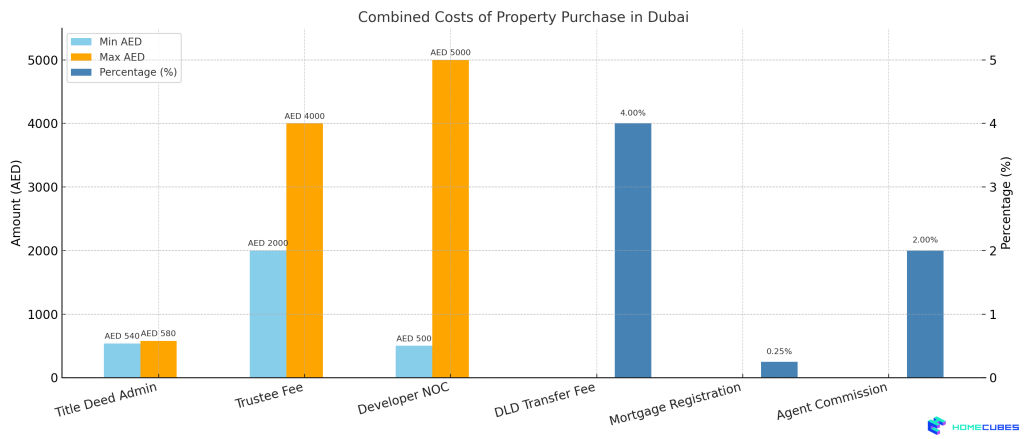
| Item | Cost |
| DLD Transfer Fee | 4% of property value |
| Admin Fee | AED 580 (approximate) |
| Title Deed Issuance | AED 250 |
| Mortgage Registration (if any) | 0.25% of loan value |
| NOC from Developer | AED 500–5,000 (varies) |
Risks and Legal Safeguards
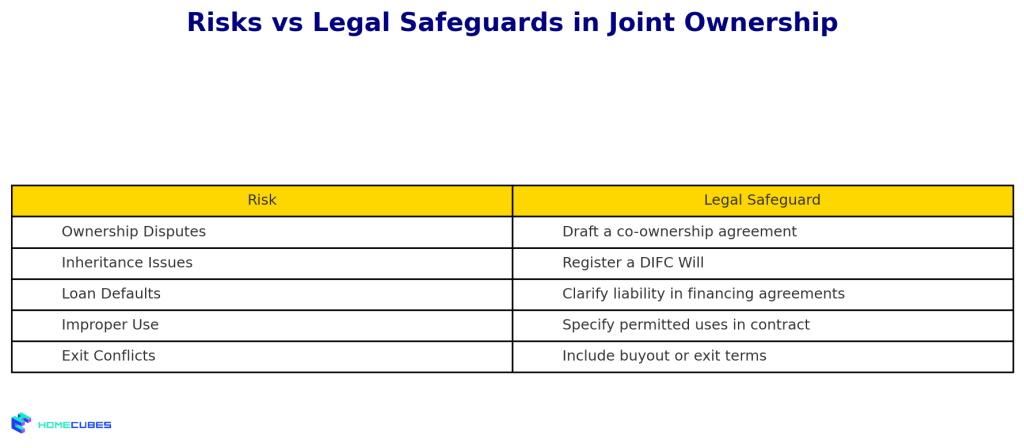
Joint ownership is beneficial but comes with several risks that require legal and procedural safeguards:
- Ownership Disputes: Without a well-drafted co-ownership agreement, disputes over property use, rental income, or sale can arise. Always formalize roles and rights in writing.
- Inheritance Issues: Non-Muslim owners should register wills with the DIFC Wills Service Centre to prevent their share from being distributed under Sharia law.
- Loan and Mortgage Defaults: One party’s default can impact all co-owners if the mortgage is jointly signed. Ensure liability is clearly defined in financing documents.
- Involuntary Transfer of Shares: In case of divorce, bankruptcy, or death, shares may be transferred to third parties unless safeguarded by legal provisions.
- Improper Use of Property: Specify how the property may be used (e.g., rental, residence, commercial) in your agreement to avoid misuse.
- Lack of Exit Strategy: If one party wants to sell, pre-agree on how exit terms and valuation will be handled.
Hiring a lawyer for drafting agreements, mediation, and future-proofing ownership is highly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I register a Dubai property jointly with my spouse?
A: Yes. Spousal co-ownership is common. Make sure to define ownership percentages clearly.
Q2: How many people can co-own a property?
A: Up to four individuals per property as per DLD regulations.
Q3: Can one party sell their share later?
A: Yes, but the other co-owners typically hold the first right of refusal.
Q4: Is shared property ownership allowed for off-plan properties?
A: Yes, registration starts via Oqood and is finalized with DLD after completion.
Q5: Do all owners need to be present at registration?
A: Not necessarily. A Power of Attorney can authorize one party to act on behalf of others.
Q6: How much are the registration fees for joint property ownership?
Fees include 4% of the property value as a DLD transfer fee, AED 580 in admin charges, and AED 250 for the title deed. Additional costs may include mortgage registration and NOC fees.
Q7: Who is responsible for paying the registration and administrative fees?
Typically, co-owners agree to share the fees based on their ownership ratio. However, this must be clarified and agreed upon in the co-ownership contract to avoid future conflict.
Conclusion
Jointly Owned Property Registration in Dubai offers a secure and flexible path for families, couples, and investors to co-purchase real estate in one of the world’s most dynamic markets. With robust legal frameworks, digital tools like Dubai REST and Mollak, and support from the Dubai Land Department, co-ownership has never been more accessible.
However, success hinges on clear agreements, timely documentation, and a shared understanding between parties. From ownership shares to exit strategies, aligning expectations and legal safeguards is key.
Whether you’re exploring one property with two owners in Dubai or forming a diversified co-ownership portfolio, Dubai provides the tools, infrastructure, and transparency needed for a smooth experience.
Be strategic, stay compliant, and leverage professional guidance to make your shared property journey both rewarding and risk-free.
Partner with Homecubes for Smart Co-Ownership Solutions
At Homecubes, we’re committed to helping you navigate the legal and logistical process of co-owning property in Dubai. While our real estate tokenization platform is pending final approval from VARA, we are actively building solutions tailored to joint ownership, fractional investment, and smart property management.
📩 Want to stay updated on our launch or ask questions about your joint ownership journey?
Contact us directly and our advisors will be happy to guide you — transparently and with your future in mind.
Homecubes — Simplifying Smart Property Ownership in Dubai.










