

Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Digital Frontier of Property Ownership
- Understanding NFT Virtual Real Estate
- Why Digital Land Matters
- The Mechanics Behind Virtual Property Ownership
- Key Metaverse Platforms Fueling NFT Real Estate
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Buy NFT Virtual Real Estate
- Real-World Case Study: The Rise of Decentraland and The Sandbox
- Fees, Costs, and Transaction Structures
- Risks and Challenges
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Regulatory and Legal Considerations
- Market Outlook 2025–2030
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Final Thoughts
- Work with Homecubes
Introduction: The Digital Frontier of Property Ownership
The concept of buying land that doesn’t physically exist once sounded like science fiction. Today, it’s an emerging asset class drawing attention from tech companies, investment funds, and retail investors alike.
Through blockchain technology, NFT virtual real estate allows users to buy, own, and trade parcels of digital land inside virtual worlds known collectively as the metaverse.
These properties are not just speculative assets; they’re programmable spaces for commerce, creativity, and community.
Understanding NFT Virtual Real Estate
Introducing Property Token Offerings, where real-world property meets NFTs.
🌆 Backed by land.
🔗 Secured on-chain.
🎟️ Exclusive NFT mint access soon.Enter now: https://t.co/JJaH9rMiJs
Comment “🏡” to be considered. pic.twitter.com/B9tX4HnIlq
— Mey Network (@Mey_Network) May 12, 2025
NFT virtual real estate represents digital parcels or buildings inside blockchain-based environments. Each property, which must not be mistaken with tokenized tangible asset, is a unique non-fungible token (NFT) stored on a blockchain such as Ethereum or Polygon.
These NFTs work like digital land titles, proving verifiable ownership. Owners can:
- Develop buildings or venues,
- Host virtual events or storefronts, or
- Lease and trade their assets on secondary markets.
According to the World Economic Forum, property in the metaverse combines digital creativity with tangible economic potential—blurring the line between entertainment and investment.
Why Digital Land Matters
Virtual land may be intangible, but its economics mirror physical property: scarcity, location, and utility drive value.
Key reasons it matters:
- Ownership Transparency: NFTs provide immutable proof of ownership on blockchain ledgers.
- Revenue Streams: Owners rent space, host paid events, or earn through advertising.
- Brand Presence: Companies establish virtual headquarters or showrooms.
- Portfolio Diversification: Digital land acts as an alternative investment asset.
Both McKinsey’s Value Creation in the Metaverse report (PDF) and Citi GPS: Metaverse and Money estimate multi-trillion-dollar economic potential by 2030, signaling a serious shift toward virtual economies.
The Mechanics Behind Virtual Property Ownership
Every piece of NFT virtual real estate exists as code secured by blockchain.
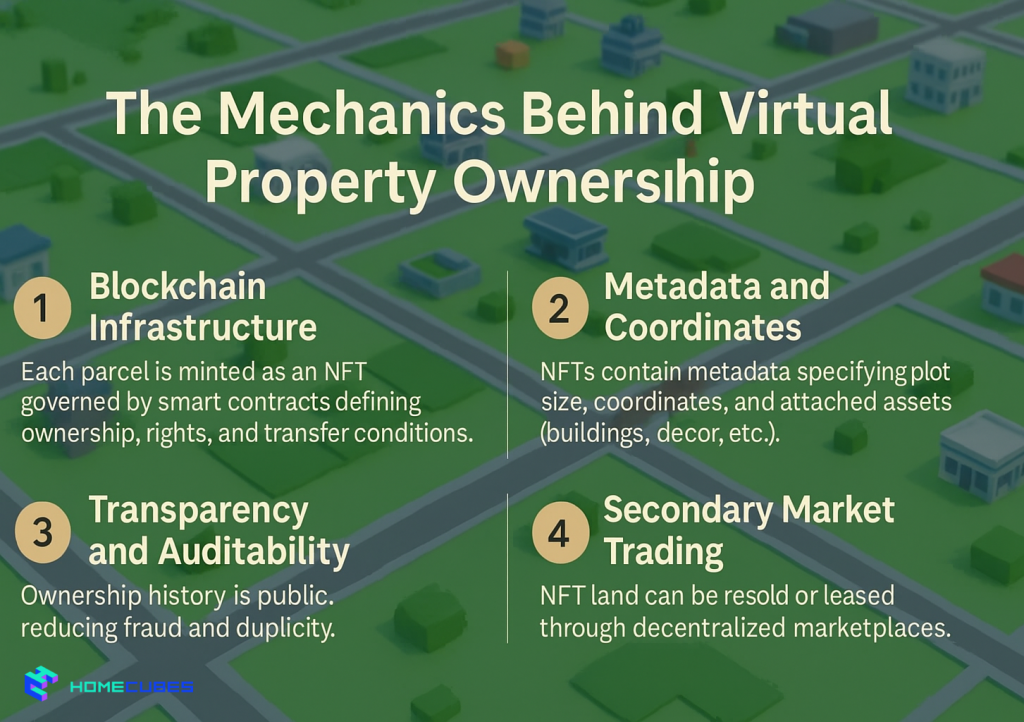
1. Blockchain Infrastructure
Each parcel is minted as an NFT governed by smart contracts defining ownership, rights, and transfer conditions.
2. Metadata and Coordinates
NFTs contain metadata specifying plot size, coordinates, and attached assets (buildings, décor, etc.).
3. Transparency and Auditability
Ownership history is public, reducing fraud and duplicity.
4. Secondary Market Trading
NFT land can be resold or leased through decentralized marketplaces.
For a clear technical explanation of parcel structure, see Decentraland Docs – Decentraland 101, which details how LAND tokens (ERC-721) hold coordinate data and ownership records.
Key Metaverse Platforms Fueling NFT Real Estate
Several ecosystems define today’s digital property market:
- Decentraland: A decentralized 3D world governed by a DAO using the MANA token.
- The Sandbox: Allows interactive game-like experiences and customizable land development.
- Somnium Space: A VR-based metaverse emphasizing immersion and avatar interaction.
- Otherside: Developed by Yuga Labs, linking NFT communities with gamified environments.
- Upland: Maps real-world cities into tokenized counterparts, merging virtual and real assets.
These platforms anchor the current NFT virtual real estate boom.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Buy NFT Virtual Real Estate

1. Choose a Platform
Select a metaverse aligned with your investment or branding goals.
2. Create a Wallet
Set up a secure wallet (MetaMask, WalletConnect) to store tokens and NFTs.
3. Acquire the Native Token
Each platform uses its own token (MANA, SAND, etc.).
4. Explore Available Parcels
Use interactive maps to browse coordinates and check ownership details.
5. Complete the Purchase
Execute the transaction via marketplace or direct sale. Ownership transfers instantly to your wallet.
6. Build or Monetize
Develop structures, host virtual stores, or hold events.
7. Secure and Back Up Keys
Enable 2FA and store seed phrases offline.
8. Stay Compliant
Understand taxation and local regulations concerning digital assets.
For practical instructions, follow The Sandbox official “How to Buy LAND” guide, which outlines wallet setup, bidding, and transfer verification.
Real-World Case Study: The Rise of Decentraland and The Sandbox
Two pioneers illustrate the momentum behind NFT virtual real estate.
- Decentraland has hosted global events like Metaverse Fashion Week and Art Week, drawing major brands such as Dolce & Gabbana.
- The Sandbox recorded land-sales volumes exceeding $350 million in 2022, with institutional participants including PwC Hong Kong and Atari.
In both ecosystems, early investors multiplied value through development, leasing, and resale.
Fees, Costs, and Transaction Structures
Unlike physical property, digital real-estate costs are mostly blockchain-driven:
- Gas Fees: For minting and transferring NFTs.
- Marketplace Commissions: 2–5 % per sale.
- Smart-Contract Deployment: Optional if you build custom features.
- Creative Assets: 3D modeling, scripts, and hosting.
- Exchange Costs: Converting crypto to fiat or vice versa.
A typical $2,000 parcel might incur $50–$150 in ancillary costs depending on network congestion.
Risks and Challenges
The opportunity is huge—but so are the risks.
- Market Volatility: NFT prices mirror crypto cycles.
- Regulatory Ambiguity: Legal ownership definitions vary by jurisdiction.
- Platform Dependency: If a metaverse closes, functionality disappears.
- Security Threats: Wallet compromises remain common.
- Liquidity Risk: Selling high-value parcels can take months.
Investors should approach NFT virtual real estate as early-stage venture exposure, not guaranteed yield.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Buying without researching project governance or user base.
- Misplacing wallet credentials.
- Ignoring smart-contract audits.
- Over-leveraging in speculative environments.
- Neglecting long-term community engagement.
Strategic diversification across multiple metaverses can mitigate exposure.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Dubai has positioned itself as a pioneer in regulating digital assets.
- The Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VAR A) oversees issuance, brokerage, and custody.
- VARA’s Rulebooks define marketing, disclosure, and consumer-protection standards.
- The Dubai Land Department (DLD) explores blockchain integration to verify digital property.
Internationally, frameworks from ADGM, Singapore, and the EU’s MiCA regulation provide additional clarity.
Homecubes aligns its future operations with these rules to ensure compliance once licensing is complete.
Market Outlook 2025–2030
By 2030, NFT virtual real estate could evolve from speculative collectibles to institutional-grade assets.
Forecast trends:
- Integration of real-world property deeds with digital twins.
- Use of AI valuation engines for virtual parcels.
- Fractional investment pools via regulated tokenization.
- Brand-driven ecosystems combining retail, art, and education.
McKinsey’s Metaverse report (Link above) notes that metaverse real-estate development could unlock $5 trillion in economic value by 2030, confirming a long-term transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can virtual land earn real income?
A: Yes — through renting, event hosting, or digital advertising.
Q: Are NFT land purchases permanent?
A: Ownership lasts as long as the blockchain and platform remain active.
Q: Can I sell or transfer my NFT property?
A: Absolutely; it’s fully tradable on decentralized marketplaces.
Q: What currencies are used?
A: Typically ETH, MANA, or SAND, depending on the platform.
Q: Can NFT real estate be fractionalized?
A: Yes — fractional NFTs allow shared ownership, similar to REIT units.
Final Thoughts
NFTs are redefining ownership in ways few imagined a decade ago. NFT virtual real estate transforms how people experience, invest in, and monetize digital spaces.
Yet investors should temper excitement with discipline—ensuring purchases are grounded in solid technology, community, and compliance.
As the metaverse evolves, Dubai’s proactive stance and legal clarity position it as a global hub for regulated digital-property innovation.
Work with Homecubes
At Homecubes, we guide investors through the intersection of real estate and blockchain. Our expertise spans tokenization, fractional ownership, and NFT virtual real estate strategy.
We have applied for our VARA license, which is under review. Once granted, we’ll launch a fully compliant platform connecting global investors to tokenized real-estate and metaverse opportunities.
If you’d like expert insights or early access to upcoming initiatives, contact Homecubes.
Homecubes — Bridging traditional property and blockchain innovation, responsibly.










